Manual skills are the foundation of physical capabilities‚ enabling individuals to interact with their environment through hands-on tasks․ These skills encompass a wide range of activities‚ from using tools to crafting objects‚ and are vital for problem-solving and creativity․ Developing manual skills fosters independence and enhances overall dexterity‚ making them essential for everyday tasks and professional endeavors․
1․1 Definition and Overview
Manual skills refer to the physical and functional abilities required to perform tasks that involve the use of hands‚ tools‚ and other physical equipment․ These skills are essential for executing practical activities‚ from simple daily tasks to complex professional operations․ They are typically acquired through practice‚ training‚ and hands-on experience․ Manual skills encompass a broad range of capabilities‚ including tool operation‚ craftsmanship‚ and mechanical aptitude․ They are fundamental for problem-solving‚ creativity‚ and efficiency in various industries and everyday life․ Developing these skills enhances dexterity‚ precision‚ and the ability to manipulate objects effectively‚ making them a cornerstone of human productivity and innovation․

1․2 Importance of Manual Skills in Daily Life
Manual skills are vital for navigating everyday tasks efficiently․ They enable individuals to perform activities such as cooking‚ repairing objects‚ and using tools‚ which are essential for independence․ These skills enhance problem-solving abilities by encouraging hands-on learning and adaptability․ Manual dexterity also improves hand-eye coordination‚ which is crucial for tasks requiring precision․ Beyond practicality‚ manual skills foster creativity and self-reliance‚ allowing individuals to craft and innovate․ They are also linked to cognitive benefits‚ as engaging in physical tasks stimulates the brain and promotes mental clarity; In a world increasingly reliant on technology‚ maintaining and refining manual skills ensures a balanced approach to life and work․
Types of Manual Skills
Manual skills are categorized into tool-based‚ craft-based‚ and mechanical skills․ These categories involve using tools‚ creating crafts‚ and operating machinery‚ respectively‚ each requiring precision and practice․
2․1 Tool-Based Skills
Tool-based skills involve the effective use of instruments like hammers‚ screwdrivers‚ and saws to accomplish tasks․ These skills are fundamental in trades‚ DIY projects‚ and various professions․ Mastery of tool-based skills enhances precision‚ efficiency‚ and problem-solving abilities․ Proper techniques‚ safety protocols‚ and consistent practice are essential for improving these skills․ They are highly valued in industries such as carpentry‚ mechanics‚ and engineering․ By understanding how to handle tools correctly‚ individuals can complete tasks more effectively and safely․ Tool-based skills also foster creativity and adaptability‚ as they often require improvisation and innovation in challenging situations․
2․2 Craft-Based Skills
Craft-based skills involve creating or shaping objects by hand‚ often blending creativity with technical knowledge․ These skills are central to activities like pottery‚ woodworking‚ sewing‚ and jewelry-making․ They require patience‚ attention to detail‚ and a deep understanding of materials․ Craft-based skills are not only artistic but also practical‚ as they often result in functional items․ They foster personal expression and cultural preservation‚ as many crafts are passed down through generations․ Developing these skills enhances fine motor abilities and encourages innovation․ Whether for hobbies or professional pursuits‚ craft-based skills offer a rewarding way to transform raw materials into meaningful creations‚ combining artistry with manual dexterity․
2․3 Mechanical Skills
Mechanical skills involve the ability to work with machines‚ tools‚ and mechanical systems․ These skills are essential for diagnosing and repairing equipment‚ understanding mechanical principles‚ and operating machinery․ Proficiency in mechanical skills often requires a strong grasp of spatial reasoning‚ problem-solving‚ and attention to detail․ Activities such as fixing engines‚ assembling components‚ or using precision tools fall under this category․ Mechanical skills are highly valued in industries like automotive‚ manufacturing‚ and engineering․ Developing these skills enhances one’s ability to troubleshoot and maintain equipment‚ making them indispensable in both professional and everyday contexts․ They also promote logical thinking and hands-on problem resolution․

Cognitive Benefits of Manual Skills
Manual skills enhance problem-solving‚ hand-eye coordination‚ and creativity by engaging the brain in practical tasks‚ fostering mental agility and innovation through hands-on learning experiences․

3․1 Enhancing Problem-Solving Abilities
Engaging in manual tasks stimulates the brain’s problem-solving centers‚ encouraging critical thinking and adaptability․ When individuals face challenges in crafting or tool-based activities‚ they develop innovative solutions․ This process sharpens analytical skills‚ teaching how to break down complex issues into manageable steps․Manual skills also foster resilience‚ as mistakes often lead to new approaches․ The hands-on nature of these activities trains the mind to think creatively and resourcefully․ Over time‚ this enhances overall cognitive function‚ making individuals more adept at tackling problems in various aspects of life․ Thus‚ manual skills serve as a powerful tool for intellectual growth and mental agility․

3․2 Improving Hand-Eye Coordination
Manual skills play a crucial role in enhancing hand-eye coordination‚ the ability to synchronize hand movements with visual information․ Activities like tool use‚ crafting‚ or sports require precise alignment of sight and action‚ fostering this skill․ Regular practice strengthens neural pathways between the brain‚ eyes‚ and hands‚ improving dexterity and accuracy․ Enhanced hand-eye coordination benefits daily tasks‚ such as cooking or typing‚ and boosts performance in hobbies like painting or woodworking․ This skill also reduces errors in precision-based activities‚ making individuals more efficient and confident in their abilities․ Over time‚ improved hand-eye coordination opens doors to mastering new skills and excelling in various pursuits․

3․3 Boosting Creativity

Manual skills serve as a powerful catalyst for creativity‚ allowing individuals to bring ideas to life through tangible actions․ Engaging in hands-on activities like crafting‚ woodworking‚ or even cooking encourages innovative thinking and problem-solving․ The process of transforming raw materials into finished products fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivates individuals to explore new possibilities․ Manual skills also promote brainstorming and experimentation‚ as they require envisioning outcomes and adjusting techniques․ By nurturing creativity‚ these skills empower individuals to approach challenges with a fresh perspective‚ making them invaluable in both personal and professional contexts․ This creative enhancement enriches overall cognitive function and inspires continuous learning․

Manual Skills in Education
Manual skills play a vital role in education‚ fostering hands-on learning and enhancing problem-solving abilities․ They integrate seamlessly with STEM and traditional subjects‚ promoting critical thinking and creativity․
4․1 Role in STEM Education
Manual skills are integral to STEM education‚ bridging theoretical knowledge with practical application․ They enable students to design‚ build‚ and test projects‚ fostering innovation and critical thinking․ By engaging in hands-on activities‚ learners develop problem-solving abilities and enhance their understanding of scientific and engineering concepts․ Manual skills also encourage collaboration and creativity‚ preparing students for real-world challenges in technology and engineering fields․ Incorporating these skills into STEM curricula ensures a well-rounded education‚ equipping students with both intellectual and practical competencies essential for future careers․
4․2 Integration into Curriculum
Integrating manual skills into the curriculum enhances learning by combining practical activities with academic concepts․ Schools are increasingly incorporating hands-on projects‚ such as woodworking‚ robotics‚ and crafting‚ to develop students’ dexterity and creativity․ These activities are often cross-curricular‚ linking subjects like math‚ science‚ and art․ For example‚ building models in geometry class or creating prototypes in engineering courses․ This approach not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also prepares students for real-world applications․ By prioritizing manual skills‚ educational institutions foster a holistic development of abilities‚ ensuring students are equipped with both intellectual and practical competencies to thrive in an evolving world․

Manual Skills in Career Development
Manual skills significantly enhance career prospects by fostering adaptability and problem-solving abilities․ Professions requiring hands-on expertise‚ such as trades and craftsmanship‚ value these skills highly‚ ensuring employability and growth․
5;1 Demand in Trades and Craftsmanship
The demand for manual skills in trades and craftsmanship remains robust‚ driven by industries requiring hands-on expertise․ Trades like plumbing‚ electrical work‚ and carpentry value precision and dexterity‚ ensuring consistent employment opportunities․ Craftsmanship‚ such as woodworking or metalworking‚ often combines creativity with technical proficiency‚ appealing to markets seeking unique‚ high-quality products․ These roles emphasize practical problem-solving and adaptability‚ making skilled individuals indispensable․ As technology evolves‚ the need for human touch in these fields persists‚ ensuring sustained demand and career stability for those proficient in manual skills․
5․2 Enhancing Employability
Manual skills significantly enhance employability by equipping individuals with practical‚ hands-on abilities sought after in various industries․ Proficiency in tasks like coding‚ data visualization‚ or customer service demonstrates versatility‚ making candidates more attractive to employers․ Industries such as technology‚ healthcare‚ and hospitality increasingly value these skills‚ as they often require both creativity and technical precision․ By mastering tools like Power BI or Tableau‚ individuals can stand out in data-driven roles․ Additionally‚ the ability to adapt and problem-solve manually fosters confidence and independence‚ traits highly regarded in the workforce․ Thus‚ developing manual skills opens doors to diverse career opportunities and strengthens professional competitiveness in a rapidly evolving job market․
Improving Manual Skills
Improving manual skills requires consistent practice‚ dedication‚ and learning from experts․ Utilizing tools like Power BI or Tableau can enhance technical abilities and foster creativity․
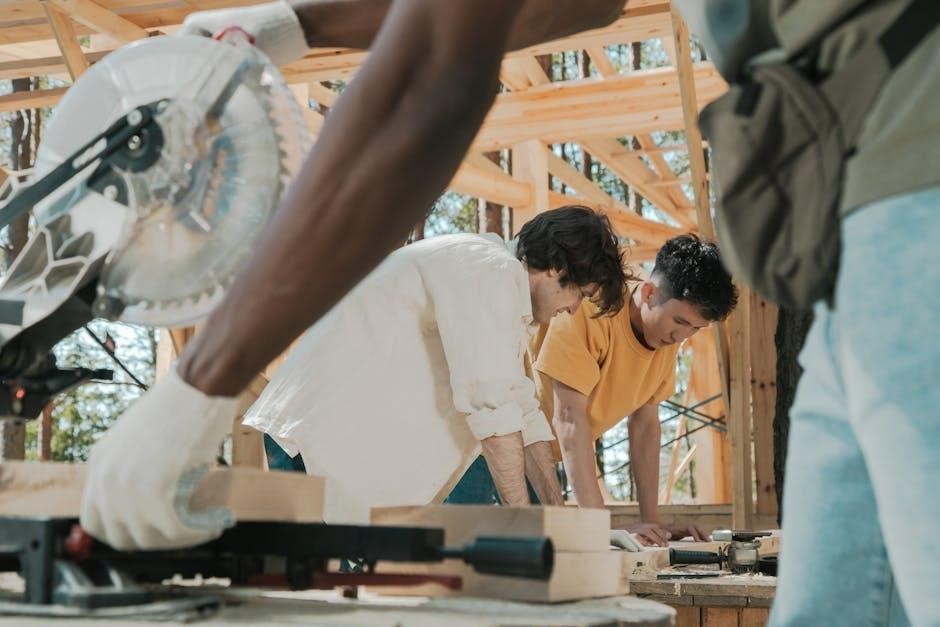

6․1 Practice and Consistency
Regular practice is crucial for refining manual skills․ Consistency helps develop muscle memory‚ allowing tasks to become second nature․ Dedication fosters precision and efficiency‚ ensuring lasting improvement over time․
6․2 Learning from Experts
Seeking guidance from experienced professionals is vital for mastering manual skills․ Experts provide valuable insights‚ shortcuts‚ and techniques honed over years of practice․ Mentorship allows learners to avoid common mistakes and accelerate their progress․ Observing how skilled individuals approach tasks can significantly enhance one’s understanding and execution․ Additionally‚ learning from experts fosters a deeper appreciation for the craft‚ encouraging a commitment to excellence․ By studying the methods of seasoned practitioners‚ individuals can refine their techniques and develop a more polished skill set․ This collaborative learning approach ensures that skills are passed down effectively‚ preserving traditional practices while incorporating modern innovations․



About the author